Introduction Of Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg: Aingo Pharma
Bacterial infections can be challenging to treat, especially when bacteria develop resistance to common antibiotics. The combination of Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg offers a robust solution by combining two active ingredients that work synergistically to combat a wide range of bacterial infections. This article delves into the uses, dosage, benefits, and potential side effects of this combination antibiotic. Whether you’re dealing with skin infections, respiratory issues, or urinary tract infections, understanding how this medication works can help you navigate your treatment options.
What is Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg?
Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg are combined in a powerful antibiotic formulation used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. Ampicillin, a well-known penicillin antibiotic, works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. However, some bacteria produce enzymes called beta-lactamases that can break down penicillins and render them ineffective. This is where Sulbactam comes into play.
- Ampicillin: A broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, making it effective against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- Sulbactam: A beta-lactamase inhibitor that prevents bacterial enzymes from breaking down Ampicillin, thus extending its spectrum of activity.
This combination is particularly useful in treating infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, which are resistant to Ampicillin alone.
How Does It Work?
Ampicillin targets and inhibits the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a vital component of bacterial cell walls. This inhibition leads to cell lysis and death. However, some bacteria produce beta-lactamase, an enzyme that deactivates Ampicillin. Sulbactam acts as a beta-lactamase inhibitor, protecting Ampicillin from degradation. This dual action allows the combination to effectively combat a wider range of bacteria, including those resistant to Ampicillin alone.
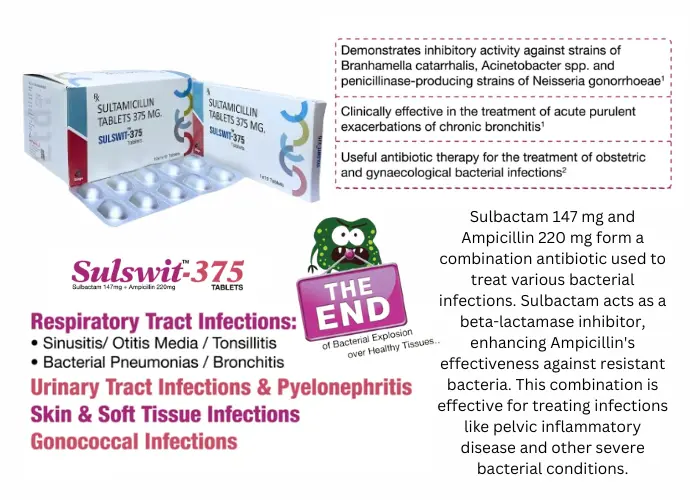
Uses of Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg
This combination antibiotic is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Effective against conditions like bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinusitis.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Useful in treating cellulitis, abscesses, and wound infections.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Effective against common UTI pathogens, including Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.
- Intra-abdominal Infections: Useful in treating conditions like peritonitis and infections associated with gastrointestinal surgeries.
- Gynecological Infections: This combination antibiotic can treat infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Bone and Joint Infections: Useful in treating osteomyelitis and septic arthritis.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s age and kidney function. Doctors commonly administer this combination intravenously, but they can also give it intramuscularly in certain cases.
Typical Dosage Guidelines
- Adults and Children Over 12: The usual dosage ranges from 1.5 g to 3 g (combination of Sulbactam and Ampicillin) every 6 hours.
- Children Under 12: Doctors typically calculate the dosage based on body weight, generally ranging from 100 mg/kg/day to 200 mg/kg/day, divided into equal doses every 6 hours..
For patients with renal impairment, dosage adjustments may be necessary. Always consult your healthcare provider for precise dosing recommendations.
Benefits of Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg
This combination offers several benefits over single-agent antibiotic therapy:
- Extended Spectrum of Activity: Sulbactam extends Ampicillin’s activity to cover beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, making it effective against a broader range of pathogens.
- Synergistic Action: The combination enhances the overall antibacterial effect, making it more effective in treating mixed infections.
- Reduced Resistance: Combining a beta-lactam antibiotic with a beta-lactamase inhibitor reduces the likelihood of bacterial resistance.
- Versatile Application: Suitable for treating various infections, from mild to severe, making it a valuable tool in clinical settings.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg can cause some side effects. Being aware of these can help you manage any potential issues.
Common Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are the most commonly reported side effects. Taking the medication with food can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Skin Reactions: Rash and itching may occur, particularly in patients with a history of allergies.
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site can occur with intramuscular administration.
Serious Side Effects
- Allergic Reactions: Severe reactions like anaphylaxis are rare but require immediate medical attention. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and severe rash.
- Liver Toxicity: Elevated liver enzymes and jaundice are rare but possible.
- Hematologic Effects: Rare cases of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia have been reported.
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Precautions and Considerations
- Medical History: Inform your healthcare provider of any pre-existing conditions, particularly liver or kidney disease.
- Drug Interactions: Sulbactam and Ampicillin can interact with other medications, including oral contraceptives, anticoagulants, and other antibiotics. Always inform your healthcare provider of all medications you are taking.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The safety of this combination during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
FAQs
- Q: Can I take Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg orally?
A: This combination is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly and is not available in oral form.
- Q: What should I do if I miss a dose?
A: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to the time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
- Q: Is it safe for children?
A: Yes, but the dosage must be carefully adjusted based on the child’s weight and the severity of the infection. Always consult a pediatrician for appropriate dosing.
Conclusion: Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg
Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg is a potent combination antibiotic that offers broad-spectrum activity against various bacterial infections. Its dual mechanism of action, combining a beta-lactam antibiotic with a beta-lactamase inhibitor, makes it particularly effective against resistant bacteria. However, like all medications, it should be used responsibly and with the guidance of a healthcare provider. Always follow the prescribed dosage and be aware of potential side effects and interactions
Contact Information:
In conclusion, Contact Aingo Pharma if you want to know regarding Sulbactam 147 mg and Ampicillin 220 mg Therefore, Below are our contact details.